INTERNATIONAL COMMERCIAL TERMS (INCOTERMS)
When you’re shipping goods internationally, there are a few terms that you should recognize and understand. INCOTERMS are used in 31 different languages, and you can find them in sales contracts as well as letters of credit.
WHAT ARE INCOTERMS?
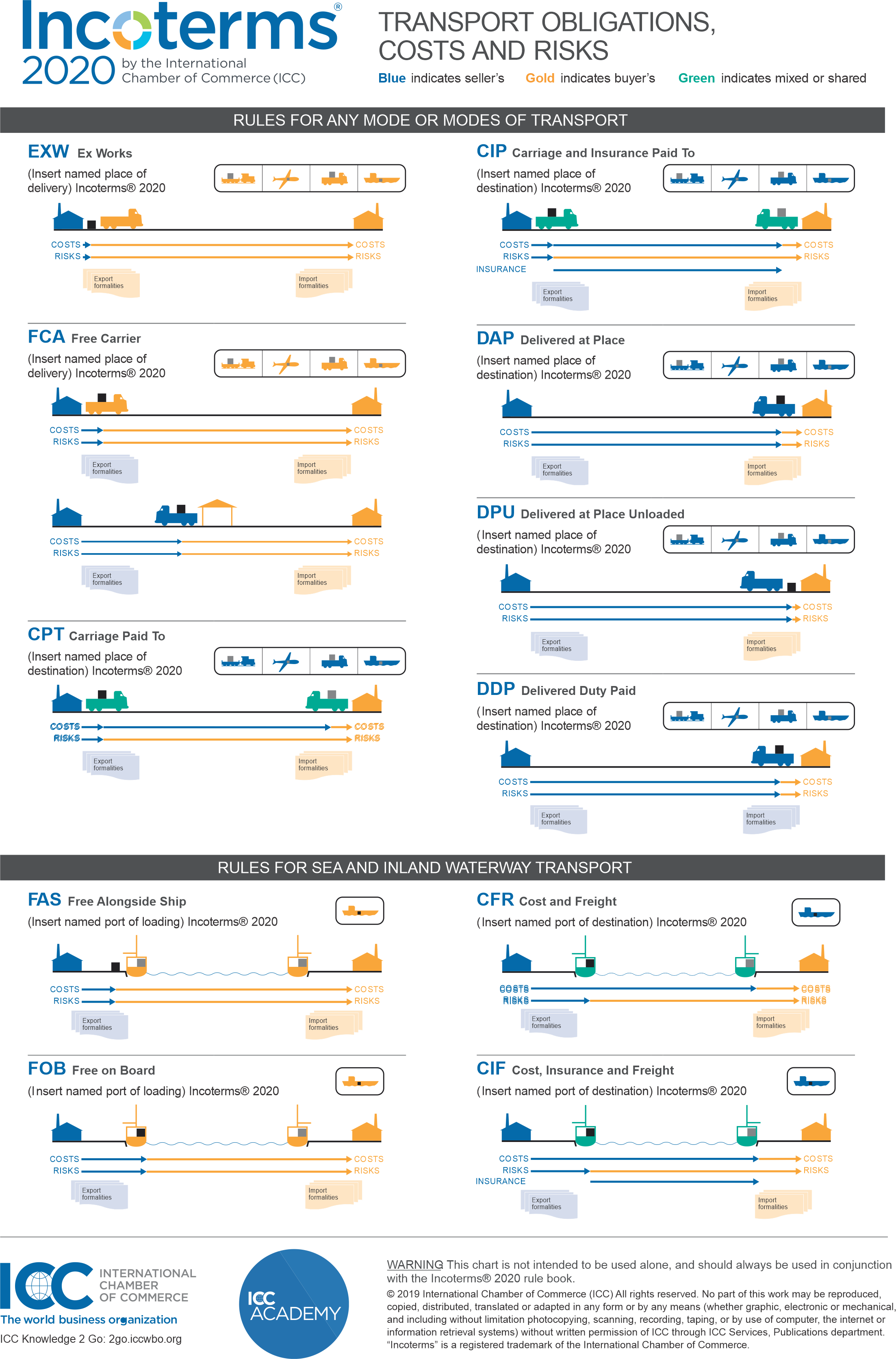
INCOTERMS are property of the International Chamber of Commerce and can be broken down into 4 categories: E, F, C, and D terms. Each INCOTERM is a code represented by three letters and a location. E terms refer to situations where the buyer can access the goods at the seller’s premises, while F terms involve the seller delivering the goods to a carrier. With C terms, the exporter arranges the shipping of the goods but isn’t responsible for damage. When the seller is responsible for both cost and risk, D terms are used.
HOW ARE INCOTERMS USED?
Language is important when you’re making a deal, but things can get confusing when each party speaks a different one. INCOTERMS keep everyone on the same page and describe the nature of the transaction. You would use different INCOTERMS for different types of transportation. Some work for any kind of transportation, while others are only applicable to water transportation.
WHY INCOTERMS ARE IMPORTANT?
It’s crucial that you are as clear as possible when working on a deal that involves international shipping, INCOTERMS lay out the costs and risks in each transaction and define what each party is responsible for. These terms help keep both sides on the same page, and they help to ensure that the goods are delivered safely and efficiently.
BASICS OF INCOTERMS:
- Owned by International Chamber of Commerce
- Standard Trade Definitions, available in 31 languages
- Used by customs and banks
- Found in sales contracts and letter of credit
- Current edition is INCO 2020
INCOTERMS are a set of three-letter standard trade terms most commonly used in international contracts for the sale of goods. First published in 1936, INCOTERMS provide internationally accepted definitions and rules of interpretation for most common commercial terms.
WHAT IS THE IMPORTANCE OF INCOTERMS WHEN QUOTING?
Provides clarity about the underlying commercial transaction. INCOTERMS inform the sales contract by defining the respective obligations, costs and risks involved in the delivery of goods from the Seller to the Buyer.
INCOTERMS rules are grouped into 4 categories:
- The “E” term: (EXW) – The only term where the seller/ exporter makes the good available at his own premises to the buyer/ importer.
- The “F” terms: (FCA, FAS and FOB) – Terms where the seller/ exporter is responsible to deliver the goods to a carrier named by the buyer.
- The “C” terms: (CFR, CIF, CPT and CIP) – Terms where the seller/ exporter/ manufacturer is responsible for contracting and paying for carriage of the goods, but not responsible for additional costs or risk of loss or damage to the goods once they have been shipped.
- The “D” terms: (DAF, DES, DEQ, DDU and DDP) – Terms where the seller/exporter/manufacturer is responsible for all costs and risks associated with bringing the goods to the named place of destination.